A Comprehensive Guide on Adding Custom Python Libraries to AWS Lambda
Are you just starting your journey with AWS Lambda and Python? You’ve probably realized that AWS Lambda’s default environment doesn’t include all the libraries you might need for your project. Don’t worry; we’re here to help you understand how to add external libraries to your AWS Lambda function in a simple and straightforward way.
In this beginner’s guide, we will walk you through the process step by step. By the end of this article, you’ll be able to enhance your Lambda functions with the power of external libraries.
Step 1: Understand Your Environment
Before we dive into the how-tos, let’s quickly understand AWS Lambda’s environment. Lambda uses Amazon Linux as its underlying operating system. So, any external libraries you add must be compatible with this environment.
- Runtime Compatibility: Ensure your Python version (e.g., Python 3.9) in Lambda matches the version you use to build your package.
- Architecture Consideration: Lambda supports x86_64 and arm64 (Graviton2) architectures. Always build your packages accordingly.
Step 2: Prepare Your Library
First, you need to prepare your external library. From the official documentation website of the library:
- Download the .tar.gz or .whl version of the entire package.
- Install the package locally inside a directory using the following command (use your virtual environment or Docker for Amazon Linux compatibility)
- Zip the contents of this folder (not the folder itself)
Step 3: Adding the Layer to AWS Lambda
Via AWS Console:
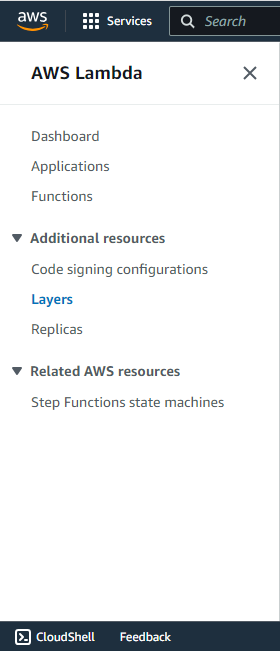
- Go to AWS Lambda > Layers.
- Click Create Layer.
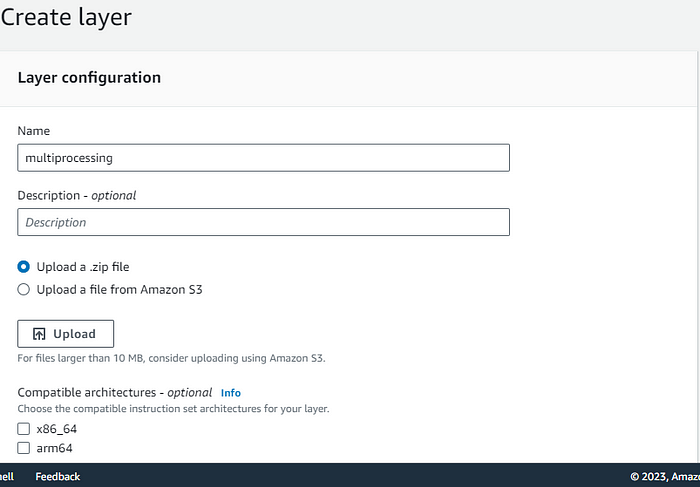
- Enter: Name of the layer (e.g., numpy-layer).
- Upload your .zip file from the local system. (For packages above 10 MB, it's better to upload the ZIP to AWS S3 and refer from there.)
- Select the compatible runtime(s) (e.g., Python 3.9).
- Choose architecture(s) as per your Lambda function (x86_64 or arm64).
- Once the layer is created, go back to your Lambda function:
- In the Function Overview, click Layers > Add a layer > Custom Layers.
- Select the layer and version you just uploaded.
Your custom layer is now successfully attached to your Lambda function.
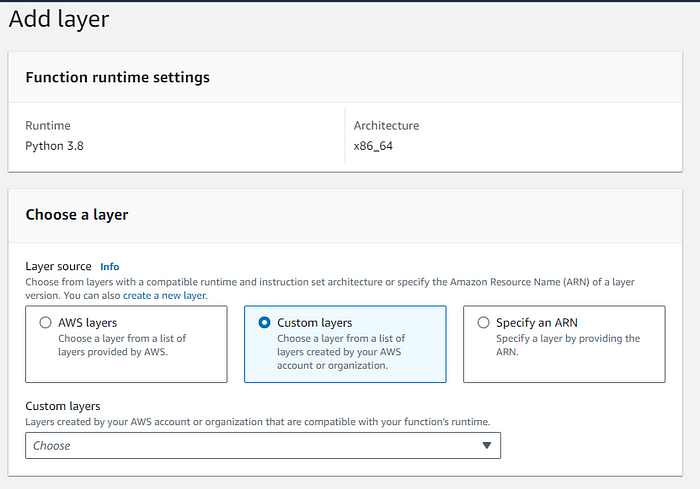
Where to Find the Custom Layer
The newly added layer will appear under:
AWS Lambda > Layers > Custom layers
You can view versions, update the ZIP file, or manage runtime compatibility from here.
Conclusion
Adding external libraries to your AWS Lambda functions can significantly expand your capabilities. Whether you're using Pandas for data analysis, NumPy for numerical operations, or Requests for API calls—creating and using layers makes it seamless.
By leveraging Python’s flexibility and AWS Lambda’s scalability, you can build robust, high-performance serverless applications without being limited by the default runtime.





