What is the cloud?
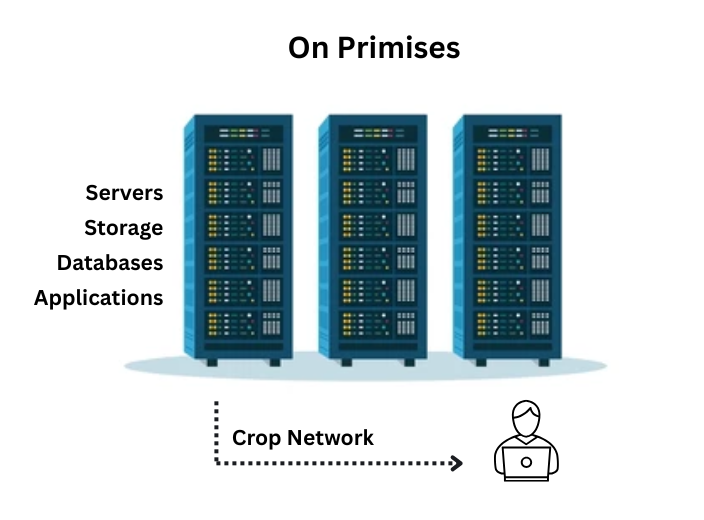
The cloud for most people is just a place of online storage, content streaming and online applications. For business this definition changes as a platform and infrastructure placed in a remote location.
Now to the more specific question: what a cloud in the context of AWS is. To answer that question, as the figure shows AWS provides IT resources and applications over the internet. Amazon Web Services is a subsidiary of Amazon that provides on-demand cloud computing platforms and APIs to individuals, companies, and governments, on a metered pay-as-you-go basis.
AWS owns and maintains network-connected hardware. We can provision and use what you need the resources provided as and when required and can be optimized as the requirements change. These resources are nothing but data centers that have already been present on premises for decades. AWS makes all these resources remote and thus eliminates their maintenance and management of the resources. This eliminates the drawbacks of an on-premises infrastructure. It also rescues the manpower involved and requires other resources involved in their functioning.
AWS owns and operates a global network of secure, network-connected data centers, which removes the burden from businesses of having to manage physical hardware themselves. This infrastructure allows organizations to provision exactly the resources they need, precisely when they need them, and to scale those resources up or down in real-time based on changing traffic or workload demands. By doing so, businesses pay only for what they use—eliminating the need for large upfront capital expenditures on servers and infrastructure. This flexibility not only reduces costs but also improves operational agility and responsiveness.
What Makes AWS Cloud Different?
The AWS maintains its own worldwide network of secure data centers with network connectivity, which absolves businesses of the trouble of maintaining physical hardware on their own. Provisioning only the resources they require, in real-time, when they require and on the fly scale the resources up or down of an organization on demand, this is what this infrastructure offers. This way businesses will no longer be obliged to buy what they do not need besides the incurring of unnecessary capital investments in servers and infrastructure. Such flexibility does not simply lower the cost, but increases the operation agility and responsiveness.
Benefits of AWS cloud
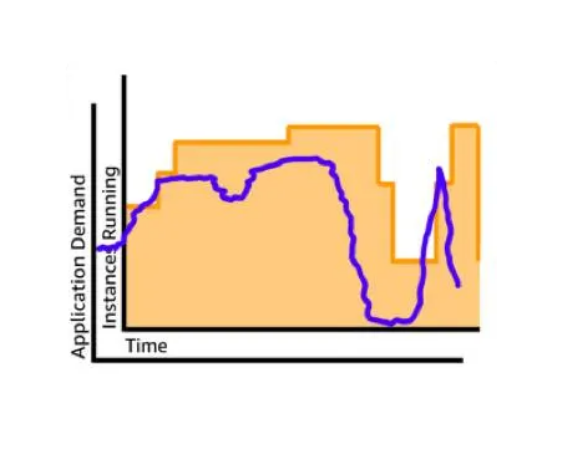
- Cost Efficiency and Pay-as-You-Go : The traditional models of IT are capital-intensive with respect to hardware and capacity investments. These tend to cause over-provisioning and consequently unused resources and wastage of finances. Conversely, the problem of under-provisioning results in performance problems and service disruption. AWS addresses this through on-demand scalability whereby you only get charged the resources you consume and resource allocation is dynamic in nature. This will promote optimality of resources use and expenditures.
- Agility and Fastness : Using AWS allows the provisioning of new resources to take a few minutes as opposed to days or weeks. This allows companies to innovate, design, and deploy applications and be ahead of the market. There are no longer procurement delays that make testing of new ideas a long process.
- Quality and Regional Accessibility : The AWS data centers are distributed over many geographic regions and availability zones providing high availability and fault tolerance. This guarantees continuity of business, recovery of disaster and enhanced performance of the application across borders.
- Security and Compliance: AWS attaches great value to security, thereby making it a reliable option even to the highly security-conscious organizations across the globe. The platform is developed with multi-disciplinary obligation to secure data, applications, and infrastructure in various layers of security. It provides end to end encryption so that data should be safe during transfer as well as at rest. Another service of the AWS is the rich identity and access management (IAM) that enables companies to manage resource access by who, and execute it on what term. The system consists of continuous monitoring and threat detection that serves a predictive purpose of identifying and responding to vulnerabilities. Moreover, AWS complies with various international standards and certification, such as ISO 27001, SOC 1/2/3, HIPAA, GDPR, etc., allowing organizations to be sure in the content of their data and hold it in an integrity-bound and regulatory-compliant manner.
- Agility and Creativity : AWS has a flexible background that accommodates both old systems and emerging technologies such as AI, machine learning, and IoT. It is compatible with every popular programming language and structure, which makes it easy to integrate. Businesses can transform, delivering innovations faster, scale their applications easily, and compress time to market, with tools such as AWS Lambda, SageMaker, Redshift and ECS.
- Automation Automation and DevOps : AWS infra-as-code tools The approach of AWS to infrastructure as code is enhanced by tools such as AWS CloudFormation and Terraform. When used together with services, such as CodePipeline, and CodeDeploy, and AWS CLI, deployment pipelines can be easily automated, DevOps can be applied either in the entirety or through CI/CD processes.
- Data Management and Storing With Amazon S3 object store, Amazon RDS and NoSQL store with DynamoDB, Amazon provides a comprehensive set of scalable, secure and highly available data services. This makes it suitable in the construction and management of data lake, warehouses, and analysis pipelines.

Why Choose Accrevent Solutions for AWS Cloud Services?
AWS enjoys and manages a network networked data centers set up all around the world and this relieves the businesses of the need to maintain their physical hardware on their own. This infrastructure enables organizations to provision just the right amount of resources required and when and where required and being able to scale it up or down in real-time due to changing traffic or work load requirements. Through such a practice, companies only end up paying what they consume- there are no huge capital investments to be made in servers and infrastructure. Such elasticity does not only diminish the costs but also raises the flexibility and responsiveness of operations.






