Flask and React are a powerful combination for building modern web applications. Flask, a lightweight Python web framework, provides a robust backend, while react, a popular JavaScript library, enables dynamic and responsive frontend interfaces. In this guide, we will cover the basics of setting up a Flask backend with a React frontend, along with a flow diagram to help visualize the integration.
Why Choose Flask and React?
Flask and React complement each other well, allowing for efficient full-stack development. Here’s a comparison of their strengths and limitations:
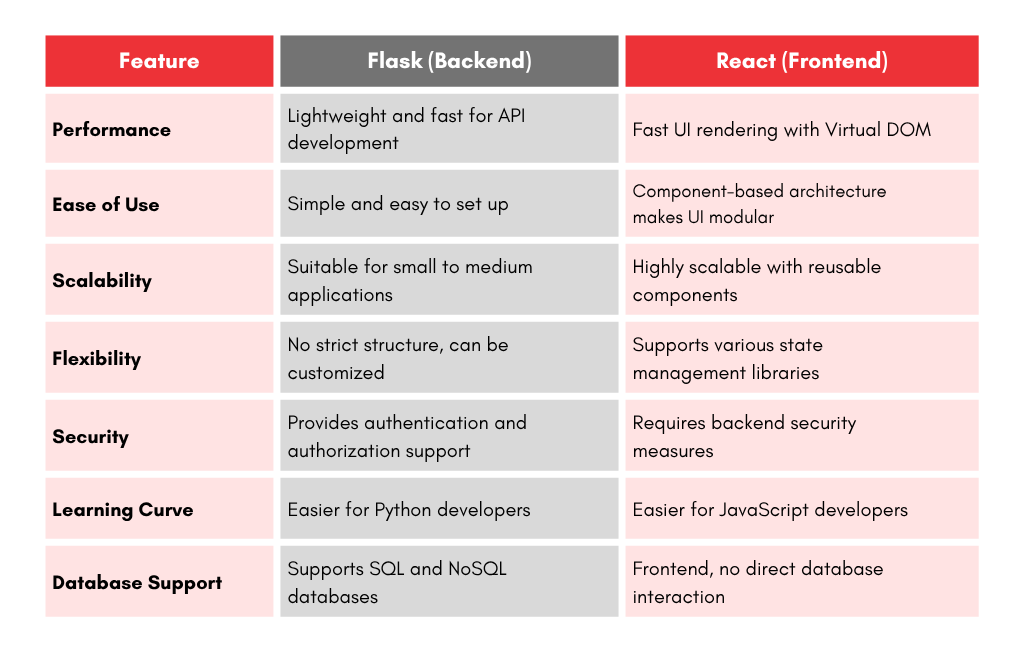
Pros and Cons of Using Flask and React Together
✅ Pros
- Clear separation of concerns: Backend and frontend are independent, making it easier to manage and scale.
- Flexible development: Developers can work on the front end and back end separately.
- Fast API development: Flask’s lightweight nature allows quick REST API development.
- Modern UI: React enables dynamic and highly interactive user interfaces.
- Cross-platform compatibility: Works across web and mobile applications.
- Large community support: Both Flask and React have strong developer communities.
- Reusable components: React’s component-based architecture promotes code reusability.
- Rapid prototyping: Flask allows quick API prototyping, while React accelerates UI design.
❌ Cons
- Requires setup and configuration: Flask and React need to be connected through an API layer.
- Higher learning curve: Developers must be familiar with both Python (Flask) and JavaScript (React).
- Data fetching complexity: Managing API calls between frontend and backend can add complexity.
- Deployment challenges: Requires proper configuration to serve React through Flask efficiently.
- Debugging overhead: Troubleshooting issues between the frontend and backend can be time-consuming.
- Performance bottlenecks: Inefficient API handling can slow down the application
React and Flask Development Tools and Libraries
Essential Development Tools
To set up a smooth development environment for Flask and React, you’ll need:
- Python & Flask: Install Flask and other Python dependencies using pip.
- js & npm/yarn: Required for React application setup and package management.
- Virtual Environment (venv): Helps isolate backend dependencies.
- Code Editors: Use VS Code, PyCharm, or any preferred editor.
- Browser Developer Tools: Chrome/Firefox DevTools for debugging.
- Postman or cURL: Useful for API testing.
Commonly Used Libraries
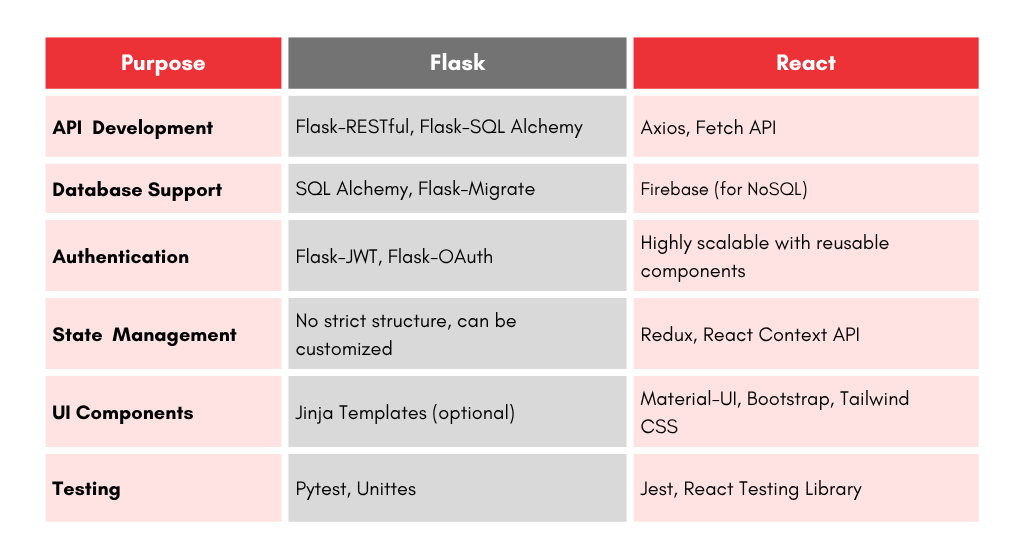
Steps to Integrate Flask with React
1. Setting Up the Development Environment

To build a full-stack application with Flask and React, you need to:
- Install Python and Flask for backend development.
- Install js and React for front-end development.
- Use CORS to allow communication between frontend and backend.
- Configure virtual environments for dependency management.
2. Creating Folder Structure
A well-organized project structure makes development smoother. Here’s a recommended structure:
project-root/
│── backend/ (Flask app)
│ ├── app.py
│ ├── requirements.txt
│ ├── build/ (React production build)
│── frontend/ (React app)
│ ├── src/
│ ├── public/
│ ├── package.json
│── README.md
3. Connecting Flask and React

- Develop a REST API using Flask to handle data.
- Use fetch or Axios in React to make API requests.
- Implement state management for dynamic updates.
- Configure proxy settings in React to avoid CORS issues.
- Handle error management and implement loading indicators for better UX.
4. Running the Full-Stack Application

- Start the Flask backend.
- Run the React frontend separately or serve it via Flask after building it.
- Open the browser and interact with the application.
- Ensure proper logging and debugging tools are set up.
Flow Diagram
Below is a basic flow of how Flask and React interact:

React sends requests to Flask using Fetch API or Axios, Flask processes the request, interacts with the database, and returns the response to React, which updates the UI dynamically.
Example of code setup:
Step 1: Setting Up Your Environment
Before starting, ensure you have the following installed:
- Python (preferably 3.x)
- js (includes npm or yarn)
- Flask
- React (via Create React App or Vite)
You can install Flask using:
pip install flask flask-cors
For React, you can set up a new project using:
npx create-react-app my-react-app cd my-react-app
Step 2: Creating the Flask Backend
1. Initialize a Flask App
Create a new folder for your backend and navigate into it:
mkdir flask-backend && cd flask-backend
Create a file named app.py and add the following code:
from flask import Flask, jsonify
from flask_cors import CORS
app = Flask(__name__)
CORS(app) # Allow cross-origin requests from React
@app.route('/api/message') def get_message(): return jsonify({"message": "Hello from Flask!"})
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True)
Run the Flask server:
python app.py
Your API should now be available at http://127.0.0.1:5000/api/message.
Step 3: Connecting React to Flask
1. Fetching Data from Flask in React
Inside your React project (my-react-app), open src/App.js and update it:
import React, { useEffect, useState } from 'react';
function App() { const [message, setMessage] = useState('');
useEffect(() => { fetch("http://127.0.0.1:5000/api/message") .then(response => response.json())
.then(data => setMessage(data.message));
}, []);
return (
<div>
<h1>Flask & React Integration</h1>
<p>{message}</p>
</div>
);
}
export default App;
2. Run React App
Start your React development server:
npm start
Your React app should now display "Hello from Flask!" fetched from the Flask backend.
Benefits of Flask and React Integration
- Modularity: Decoupled frontend and backend enable independent scaling and updates.
- Enhanced User Experience: React’s interactive UI paired with Flask’s efficient API ensures smooth performance.
- Microservices Compatibility: Flask can serve as a microservice backend for various frontend applications.
- Improved Maintainability: Separation of concerns leads to cleaner code and easier debugging.
- Strong Security: Flask provides authentication, while React handles frontend authorization mechanisms.
- API-First Approach: Easily extend your backend to mobile apps or other clients.
- Support for Machine Learning: Flask can integrate ML models, making AI-powered applications feasible.
Enhancements and Next Steps
Now that you have a basic integration, here are some enhancements you can explore:
- Database Integration: Use PostgreSQL, MongoDB, or SQLite with Flask SQL Alchemy.
- Authentication: Implement user authentication with JWT tokens.
- State Management: Utilize Redux or Context API for better frontend state handling.
- Deployment: Host your full-stack application using services like Heroku, Firebase, or AWS.
- GraphQL Integration: Replace REST with GraphQL for more efficient API calls.
- Containerization: Use Docker to simplify deployment and scaling.
- Testing and Debugging: Implement unit and integration testing for a robust application.
- Performance Optimization: Use caching, database indexing, and efficient API handling to improve performance.
Use Cases of Flask and React Integration
- Data-Driven Dashboards
- Scenario: A company wants to analyze customer feedback and generate sentiment analysis reports.
- Solution: Flask handles the data processing and API, while React presents interactive charts and tables.
- Example: Business intelligence dashboards, financial reports.
- E-Commerce Applications
- Scenario: An online store needs a fast, scalable frontend with secure transactions.
- Solution: Flask provides authentication, order processing, and database management, while React ensures a seamless shopping experience.
- Example: Online retail websites, digital marketplaces.
- Chat Applications
- Scenario: A business requires real-time customer support via chat.
- Solution: Flask handles WebSocket-based real-time messaging, while React updates the UI dynamically.
- Example: Live chat support, collaborative messaging platforms.
- Machine Learning-Powered Applications
- Scenario: A company wants to deploy an AI-based recommendation system.
- Solution: Flask serves machine learning models via an API, and React displays personalized recommendations.
- Example: Movie recommendation systems, fraud detection tools.
- Project Management Tools
- Scenario: A team needs a task management system with real-time updates.
- Solution: Flask handles task creation, updates, and notifications, while React provides a dynamic interface.
- Example: Kanban boards, team collaboration tools.
- Content Management Systems (CMS)
- Scenario: A company wants an easy-to-use CMS for blogs and articles.
- Solution: Flask manages user authentication and content storage, while React allows easy content editing.
- Example: Blog platforms, online documentation sites.
- IoT (Internet of Things) Applications
- Scenario: A company wants to monitor and control IoT devices remotely.
- Solution: Flask collects and processes IoT data, while React visualizes the data in real-time.
- Example: Smart home automation, industrial monitoring systems.
Example Snippets of Planex Project Management Tool:





Conclusion
By combining Flask and React, you can create scalable and interactive web applications with a strong backend and dynamic frontend. This guide provided a basic setup, but you can extend it by integrating databases, authentication, and state management tools. Flask and React offer a powerful ecosystem that supports a wide range of applications, from small projects to enterprise-level solutions. Start exploring and building your full-stack applications today!





